Photo by Vu M. Khuee / Unsplash
Primary Sector Economics
Introduction
An economy is an area where resources are used by business firms in producing goods and services to satisfy the needs and wants of people. In most of the economies, there are millions of business firms which are involved in producing different types of goods and services. The set of those businesses which share similar or related business activity, product, or service is called a sector. A sector of an economy represents a set of business firms with identical business activities, like agriculture and extraction of raw natural resources from land. In order to analyse economic activity within different sectors, economists divide an economy into various sectors that provide detailed information on how business activities affect an economy. Therefore, the sector analysis provides evidence about an economy, whether it is expanding or if some areas of an economy are facing contractions. In this article, we will explain the primary sector of economy in detail.
Major Sectors of an Economy
Even though there is a debate about the exact number of sectors that represent the business activity in an economy, mainly there are four major sectors of an economy, but these sectors can also be subdivided into different sectors.
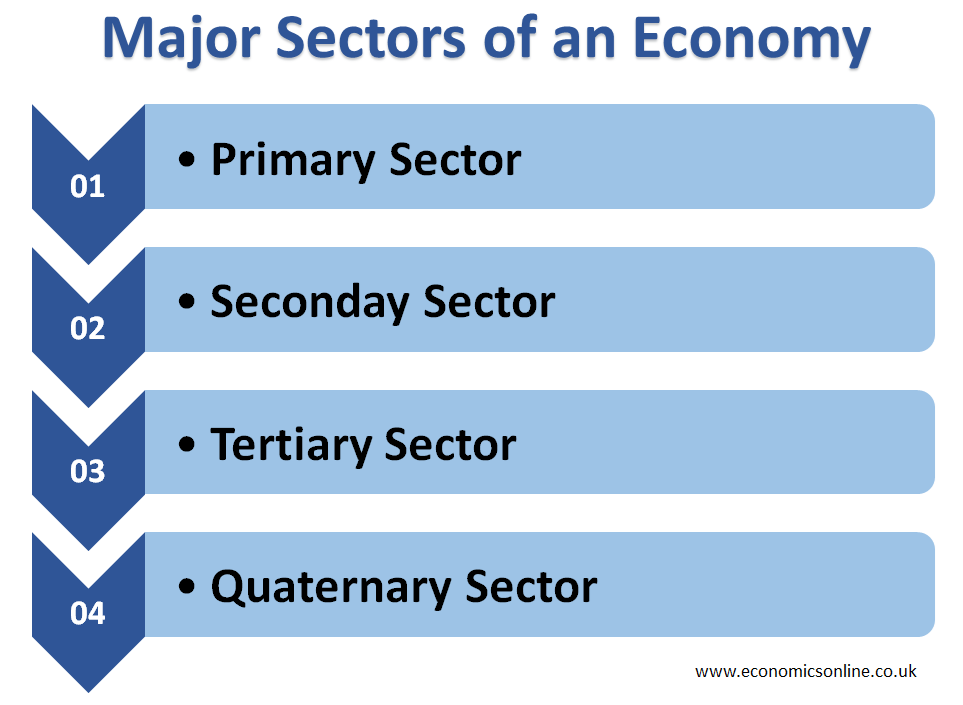
Primary Sector
It involves those companies that are involved and participate in the extraction and harvesting of raw material from the land (earth). These companies, mainly primary sector companies, are involved in those economic activities that utilise the extracted earth’s natural resources and sell them to customers or commercial businesses. Those companies that are only involved in the packaging of raw materials are also categorised as primary sector companies. Some primary sector business activities are fishing, agriculture, mining, forestry, hunting, and quarrying.
Many emerging companies are liable to have a greater amount of economic activity and employment concentrated in the primary sector as compared to more advanced economies. Alternatively, developed nations prefer to utilise machinery and technology in their primary sector economic activities. This means that the primary sector does not represent a large portion of the population’s employment.
Secondary Sector
The processing, manufacturing, and construction businesses are involved in the secondary sector. This sector produces goods from the natural resources taken from the primary sector. In secondary sector, companies perform business activities such as textile, automobile production, aerospace space, chemical engineering, shipbuilding, and energy utilities.
Tertiary Sector
The third sector is the tertiary sector, which is comprised of those business firms that provide services, like entertainment firms, retailers, and some financial organisations as well. This sector provides services to customers and businesses by selling those products that are produced by companies in the secondary sector. The tertiary sector provides services like tourism, restaurants, retail sales, transportation, distribution, healthcare services, legal services, banking, and insurance.
The tertiary sector is the largest sector in the US since the service industry holds a large share of economic activity.
Quaternary Sector
Businesses involved in intellectual activities and pursuits are included in the quaternary sector. In this sector only typical intellectual services, like technological advancement and innovation, are involved. Research and development are also included in this sector that leads to improvements to processes, like manufacturing.
These companies and firms were part of the tertiary sector, but the growth of the knowledge-based economy and advancements in technology created a separate sector, named the quaternary sector.
Businesses in this sector use technology and information to innovate and modify processes and services, causing enhancements in economic development. In the quaternary sector, companies are involved in business activities like education, consulting services, information technology (IT), and research and development (R&D).
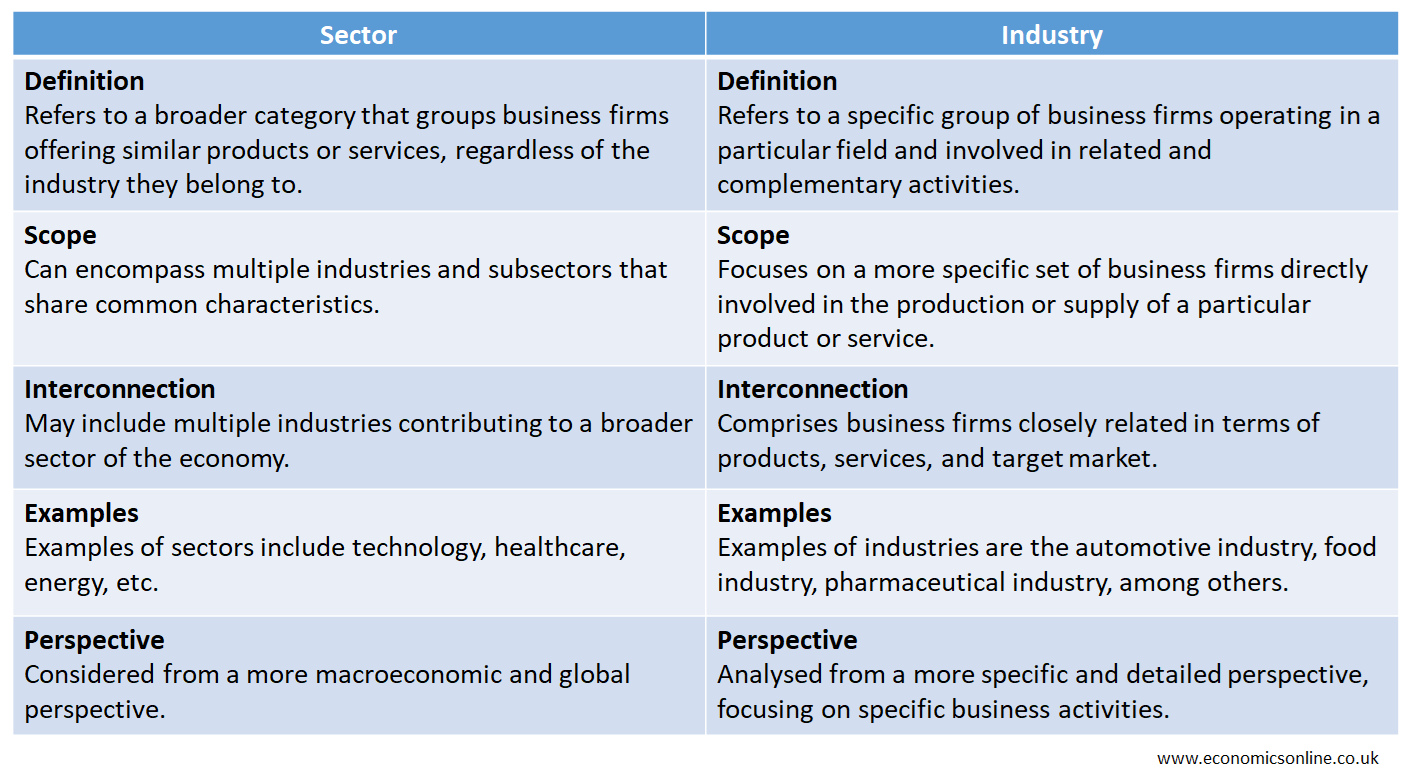
Differences between Sector and Industry
An industry is the collection of business firms which are involved in making same or similar products. For example, textile industry is composed of different textile businesses which are involved in ginning, spinning or weaving of textile products. The following table contains the main points of difference between a sector and an industry.
Categorisation for Primary Sector
The following major industries are included in the primary sector:
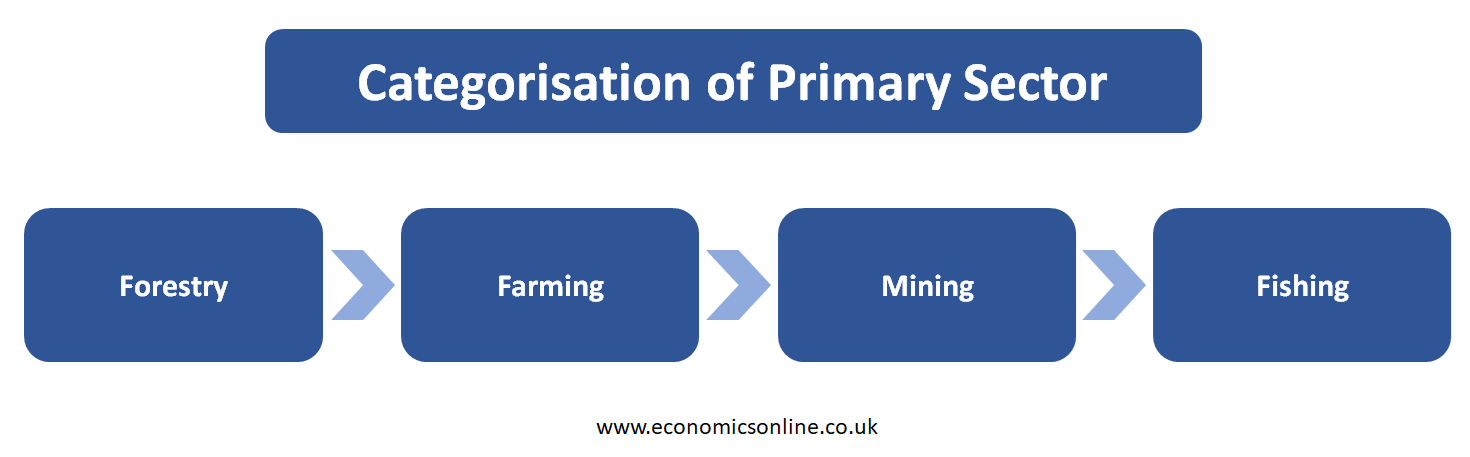
Forestry
Businesses related to forest products contribute a significant amount to world economies. Forestry is a crucial supplier of raw materials for many sectors. All types of forest sector products help address some of the basic needs of contemporary civilisation, but some work for improving worldwide human well-being.
Farming
Farmers are the ones who cultivate plants and raise animals to produce food and other items. Agriculture is a primary-sector industry, and it has the ability to produce raw food using agriculture methods. For example, the food category consists of eggs, meats, vegetables, milk, and oils. In agriculture, cotton is a raw material used to manufacture clothes.
Mining
Mining is the extraction of raw materials from the land, like minerals, sand, metals, clay, rocks, and gemstones. The most precious assets of a mining company are its raw reserves and resources. Mining is also a source of raw materials for secondary sectors as well. They use raw materials to produce and create different imported goods. Some nonrenewable resources, like natural gas, petrol, and water, are also included in the category of mining.
Fishing
It is also the world’s most critical primary business. Fishing businesses are responsible for everything from shipping and promoting fish products to preserving and processing them. Globally, industrial fish farming is the fastest growing food technology. The fish farms are now providing about half of the world’s seafood.
Advantages of Primary Sector
The following are some advantages of the primary sector:
- The primary industry is important for creating job opportunities, increasing tax incomes, and generating export revenues.
- In the primary sector, it is possible to find a worker who is eager and willing to work in considerable quantities in the developing countries with a sustainable and elastic labour supply.
- Those businesses that produce primary goods have a significant competitive advantage in many emerging economies.
Issues Related to Primary Sector
The following are some issues related to the primary sector:
Power of Monopoly
Relying on the primary sector is a common concern, and the wealth is typically distributed unevenly. When one business has a monopolistic control over the manufacturing of raw resources, they only pay their employees a small portion of the profits they earn. For example, many African rising states have still remained poverty-stricken regardless of being rich in raw resources.
Volatility
The fluctuations in the price and production are common in primary products. The price fluctuations in oil and supplies might be significant. In terms of demand, there is a lot of price inelasticity. Those governments that totally rely on a single sector or industry may face a significant loss if prices fall, which automatically causes problems for them. For example, the European Union (EU) starts helping EU agriculture by giving subsidies and price support.
Revenue from Exports
Natural resources are the ones which help a country’s economy produce and generate money for the nation’s consumption. Many developing countries took advantage of raw materials by trading gas, oil, and other useful resources and consumed the earned money for multiple initiatives to consume it on public services within their economies. For example, some oil-rich nations have taken advantage of this increased wealth to save money for the future.
Sectors and the Economy
Sectors of an economy provide information about how an economy is performing and which areas are performing better as compared to others.
Sectors in an Expanding Economy
When there is a significant increase in the purchase of raw materials, like crude oil and copper, this means that the economy is expanding. In other words, individuals and businesses tend to consume more raw materials and energy as their spending is on the rise in the expanding phase. In an expansionary economy, industries also perform well due to increased economic growth, which typically leads to an increase in construction and manufacturing. Real estate, including commercial real estate and housing, also faces an increase in sales and development in the case of an expanding economy. But when consumer confidence rises, they might increase their purchases of non-essential goods, which lead to an increase in consumer discretionary spending. However, companies included in the sectors will experience increased revenue from an expansionary economy.
Sectors in a Slowing Economy
On the other hand, if an economy is performing poorly or there are projections that economic growth will reduce in the upcoming months, only those companies that sell consumer staples sometimes experience an increase in revenue. The main reason for this correlation between a slowing economy and consumer staple stocks is that customers will likely begin to buy essential products, like paper towels and toilet paper, even in periods of less economic growth. However, investment sectors also represent a particular risk profile that may or may not attract investors. For example, during times of slowing economy, investment in the utilities sector will increase as those stocks are considered safe-haven investments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sectors are used to classify the economic activities of businesses into groupings based on the type of their business activity. Each sector depicts a different stage of economic activity in order to understand how closely the activity is attached to the extraction of natural resources. Sectors are important as they help economists and investors understand the multiple levels of economic activity and how well an economy is performing.