
Gross Wages vs. Net Wages
Introduction
In economics, labour is a factor of production, and it means the physical and mental services provided by workers in producing goods and services. The reward for labour is called a wage. There are many different types of payments made to workers, but gross wage and net wage are two main payments that firms give to their workers against their services. These terms are often used in employee’s payroll and are explained in this article.
Gross Wage
The gross wage is the amount that firms pay to its employees before interest, taxes, and payroll deductions. The gross wages consist of all forms of payments, like salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, compensations, and any other such monetary benefits, before making any deductions. The gross wages can be calculated based on the number of working hours or services provided by workers and agreed-upon rates of wages.
Gross wages consist of wages or salaries. If a person has two jobs, his gross wages are separate for each job. The gross wages play a role as the basis for deciding the net wages after tax deductions, retirement contributions, insurance premiums, and other withholdings of an individual. The precise and accurate calculation and reporting of gross wages are necessary for regulatory payroll compliance and maintaining transparency in employment reimbursement practices.
Gross wages help determine a person’s ability to make payments, particularly to homeowners or lenders, and to evaluate an individual’s income taxes. That is why gross wages is an important data point to understand and consider.
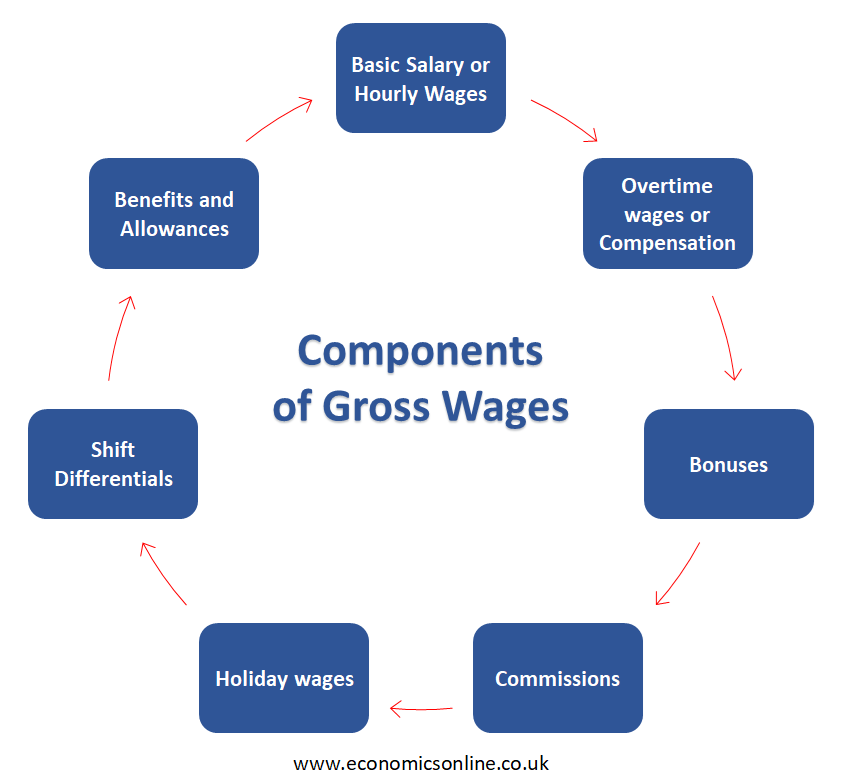
Components of Gross Wages
The following are some components of gross wages:
Basic Salary or Hourly Wages
An important component or core component of gross wages is the basic salary or hourly wages of an employee, which is the predetermined amount mentioned in the employment contract and also an important element of the individual’s compensation package.
Overtime Wages or Compensation
In some situations where employees work extra hours except their standard working hours, they may be eligible for overtime pay or compensation. Overtime wages or compensation is always given at higher rates compared to regular wages and determines gross wages notably.
Bonuses
A bonus is the amount of money paid to workers over and above their salary or wage. This variable component may be associated with employees’ performance, their achievements, particular milestones, or a good time of the year like a festival. These additional incentives provide an employee with greater financial compensation for their services.
Commissions
For those employees or individuals that are in sales or revenue-generating roles, commissions are essential in determining their gross income. A percentage of sales or revenue an individual generates is called commission. It is an additional variable and a substantial component for their overall paychecks.
Holiday Wages
A type of wage that recognises an individual’s work during holidays is called holiday wages. It is an additional component of gross compensation. The holiday wages are added to the individual’s total compensation package while realising the impact on their time.
Shift Differentials
Employees who are working non-standard shifts, such as weekends and nights, are provided with shift differentials in occupations with changing work schedules. These shift differentials mirror the additional challenges of working non-standard hours that must be wages back as a part of the gross wages.
Benefits and Allowances
Some benefits and allowances, such as transportation, meal benefits, and housing, are considered in calculating the total amount of money wages of an employee. These are not always provided as direct cash; embracing the benefits and allowances improves the overall financial situation.
Importance of Gross Wages for Employees
Gross wages are important for employees because they are used for many purposes that may matter for an individual. The following are some points that show the importance of gross wages for employees:
Helps Qualify for Loans
Gross wages are important for the approval of loans, as it is one of the criteria when applying for a loan. The gross wages should meet the minimum requirement for a loan to proceed.
Helps with Rent Housing
The gross wages also play an important role when looking for a rental house, and the homeowners assess the gross wages of potential renters in order to determine whether they are able to pay their house rents on a regular basis or not.
Determining Credit Limits
Gross wages are also required when applying for credit cards. The credit card issuers check the gross wages when determining the credit limits.
How to Calculate Gross Wages
The following are two ways to calculate the gross wages:
For Salaried Workers
The gross wages of an employee can be calculated by dividing his total amount of annual salary by the total number of pay periods per year.
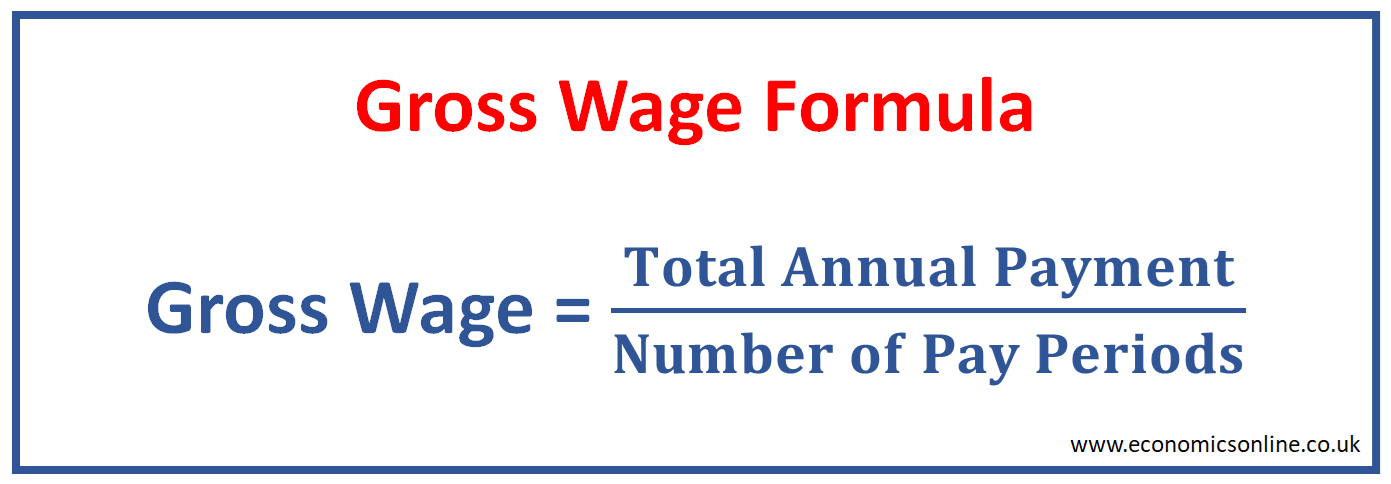
Gross Wage = Total Annual Payment / Number of Pay Periods
For example, those businesses that pay their employees on a weekly basis have 52 weeks of pay per year. If they pay a sum of $26,000 per annum, the gross wage can be calculated as:
Gross Wage per Week = $26,000 / 52 = $500
For Hourly Employees
The gross wages for hourly employees are calculated differently from those for salaried employees in the labour market. In the case of hourly employees, the gross wage is equal to the hourly rate multiplied by the number of hours worked or services rendered.
Gross Wages = Hourly Rate × Number of Hours Worked
For example, if the work rate per hour is $10 and a worker works 8 hours a day for five days a week, then this worker works for 40 hours per week. This means that this worker is paid $400 for that pay period. This value may vary if the worker works overtime.
Net Wages
The amount of money that an individual or employee takes home directly after all deductions from his/her gross wage is called net wage. The amount of net wage is the take-home pay and may be much lower than gross wages when all the deductions both below and above the line have been made. This deduction may be compulsory, optional, and possibly include income tax. These kinds of deductions mainly include charges for retirement benefits and health insurance.
Net wages vary greatly because it includes deductions, such as taxes, wage trimming, and other benefits. An individual's net wage can also be affected by factors such as tax credits, marital status, location, and the number of dependent family members.
Formula

Net Wage = Gross Wage - Deductions
Standard Deductions
The following are two standard deductions that were made from gross wages but resulted in the net wages:
Taxes
Taxes, for example, healthcare expenditure, social security, federal, state, and other local taxes affect the net wages of an individual.
Pretax
Pretax deductions are wage cuts like finance towards company-sponsored retirement plans, for example, health and dental insurance, and FSAs (flexible spending accounts).
How to Calculate the Net Wages
In order to calculate the net wage of an individual, first we need to consider all the deductions that affect the individual’s total compensation. The following are some steps that are used to subtract all types of deductions from the gross wages to determine the net wages.
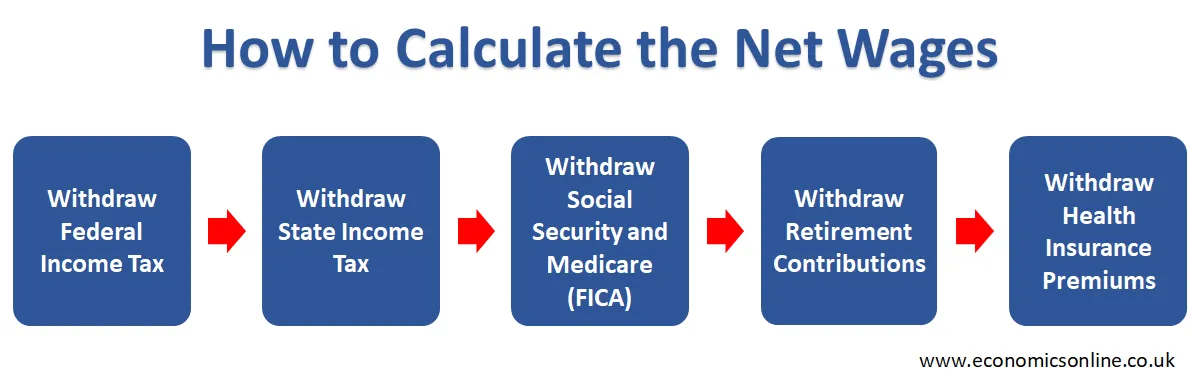
Withdraw Federal Income Tax
The first step is to deduct the federal income tax according to the individual’s or employee’s income and tax bracket.
Withdraw State Income Tax
The second step is that some states impose income taxes rather than federal income taxes, which are subtracted from employee’s gross wages.
Withdraw Social Security and Medicare (FICA)
The third step is to withdraw social security and Medicare expenses (FICA taxes) because employees are bound to pay or contribute a percentage of their earnings to social security and Medicare taxes.
Withdraw Retirement Contributions
The fourth step is to deduct retirement contributions, like 401(K)s and FSAs, before tax calculations. These are the voluntary deductions for contributions to retirement plans by employees.
Withdraw Health Insurance Premiums
The final step is to withdraw or deduct the cost of health insurance premiums that affect the net wages of employees.
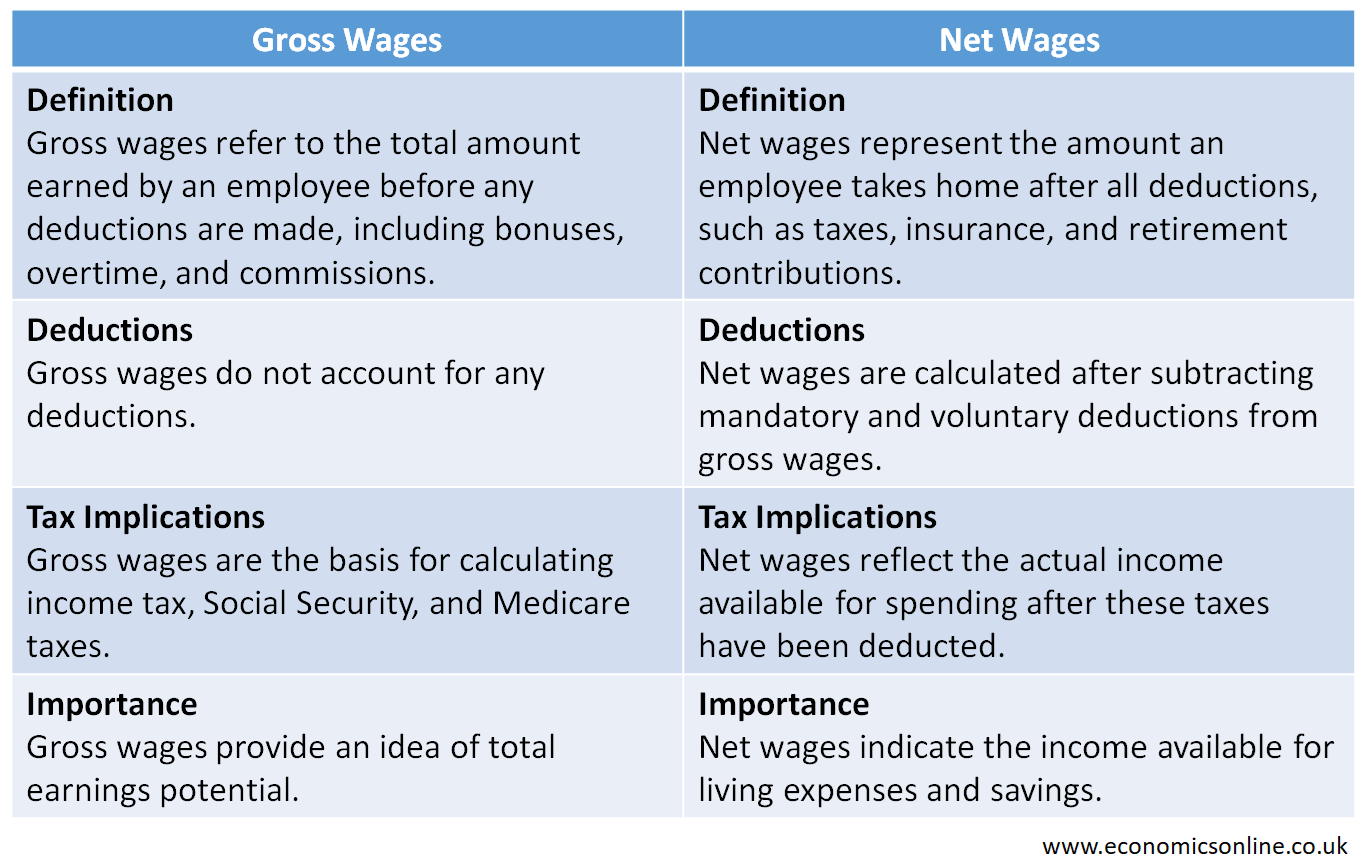
Differences between Gross Wages and Net Wages
The following table summarises the main point of difference between gross wages and net wages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both gross wages and net wages affect the employee’s income. Gross wages are the amount that an individual earns by working on either an hourly basis or a salaried basis before all kinds of deductions. The net wages are the amount that an individual earns after deducting all kinds of taxes, insurance premiums, etc. The deductions in gross wages affect the net wages of a worker.


