
Photo by Philippe Leone / Unsplash
Dependency Ratio Definition
What is the Dependency Ratio?
The proportion of the population that is dependent on the welfare state in comparison with the population of the working age is called the dependency ratio. It is also called the total dependency ratio or age dependency ratio and is an important measure of age structure of the population of a country. According to the United Nations Population Division and the World Bank, the dependency ratio is a measure of the number of dependents aged below 15 (children) and above 64 (elderly) compared with the overall population aged from 15 to 64 of a country. The dependency ratio is a demographic indicator that provides information about the number of people of non-working age compared with the number of people of working age in a country’s overall population. The dependency ratio is also used to understand the economic burden of the workforce and has consequences for taxation.
Formula
Here is the formula to calculate dependency ratio:
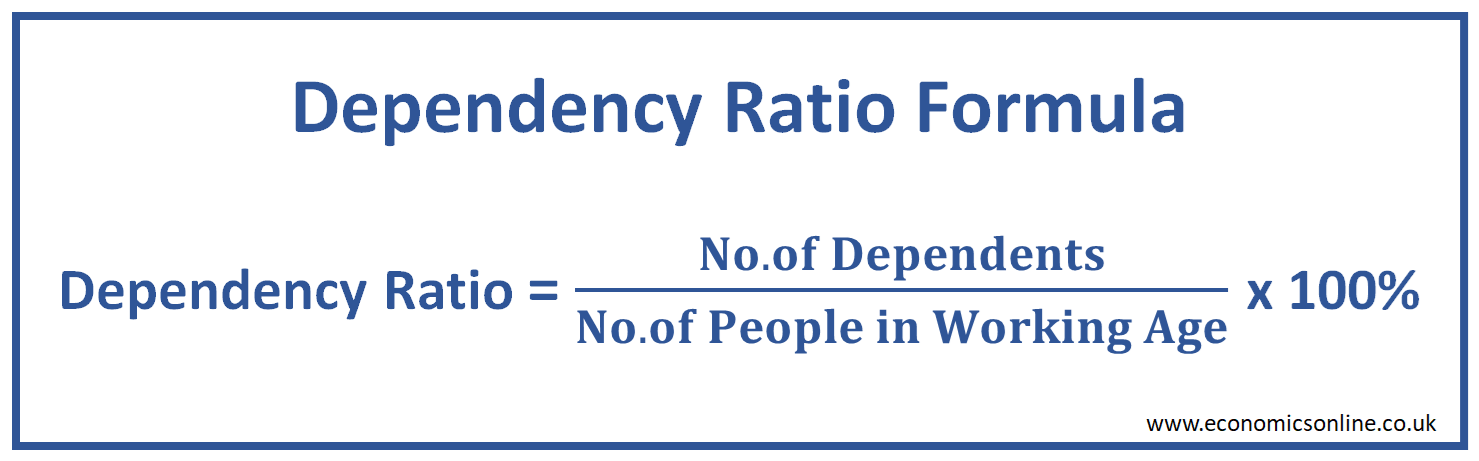
Dependency Ratio = (Number of Dependents / Number of people of Working Age) x 100%
Dependency Ratio = (Number of people in the dependent age group / Number of people in the working age group) x 100%
Understanding Dependency Ratio
The population of a country can be divided into the following two groups:
Dependent Age Group
This group is composed of children and elderly and can be further divided into two subgroups:
Children – below 15 years
Elderly – above 64 years
The number of people in the dependent age group is the sum of the population of the children (below 15) and the elderly (above 64).
Working Age Group
This group consists of people of age from 15 years to 64 years.
Now, the dependency ratio is the number of people in the dependent age group calculated as a percentage of the number of people in the working age group. Let’s understand this with the help of a simple hypothetical example. Let’s suppose that a country has a population of 800 people. In this country, there are 150 children under the age of 15, 150 elderly people over the age of 64, and 500 people in the working age group who are aged from 15 to 64. In this case, the dependency ratio is calculated as follows:
Number of people in the dependent age group = No. of Children + No. of elderly
= 150 + 150 = 300
Number of people in the working age group = 500
Dependency Ratio = (Number of people in the dependent age group / Number of people in the working age group) x 100% = (300 / 500) x 100% = 60%
A high value of dependency ratio explains that the overall economy and the economically active population face a greater burden in supporting the dependent population.
Other Types of Dependency Ratio
Other forms of dependency ratio are the youth dependency ratio and the elderly dependency ratio.
Youth Dependency Ratio
The youth dependency ratio is the number of dependents aged below 15 (youth) calculated as a percentage of the number of people in the working age group. Its formula is given below:
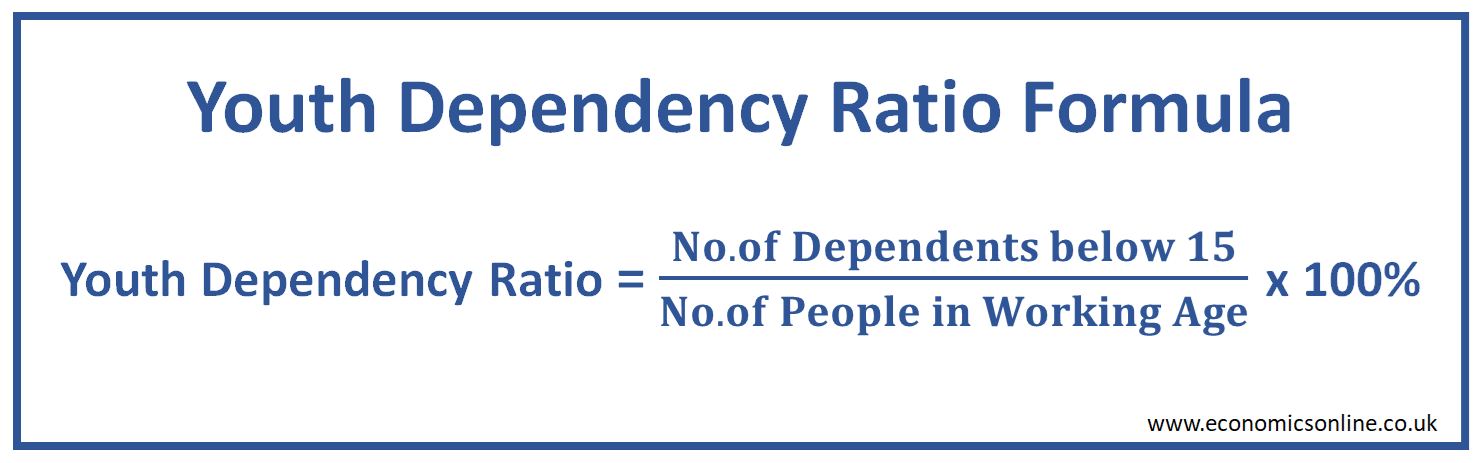
Youth Dependency Ratio = (Number of Dependents below 15 / Number of people of Working Age) x 100%
A high youth dependency ratio means a higher level of government spending in schooling and childcare.
Elderly Dependency Ratio
The elderly dependency ratio is the number of dependents aged above 64 (elderly) calculated as a percentage of the number of people in the working age group. It is also called the old-age dependency ratio. Its formula is given below:
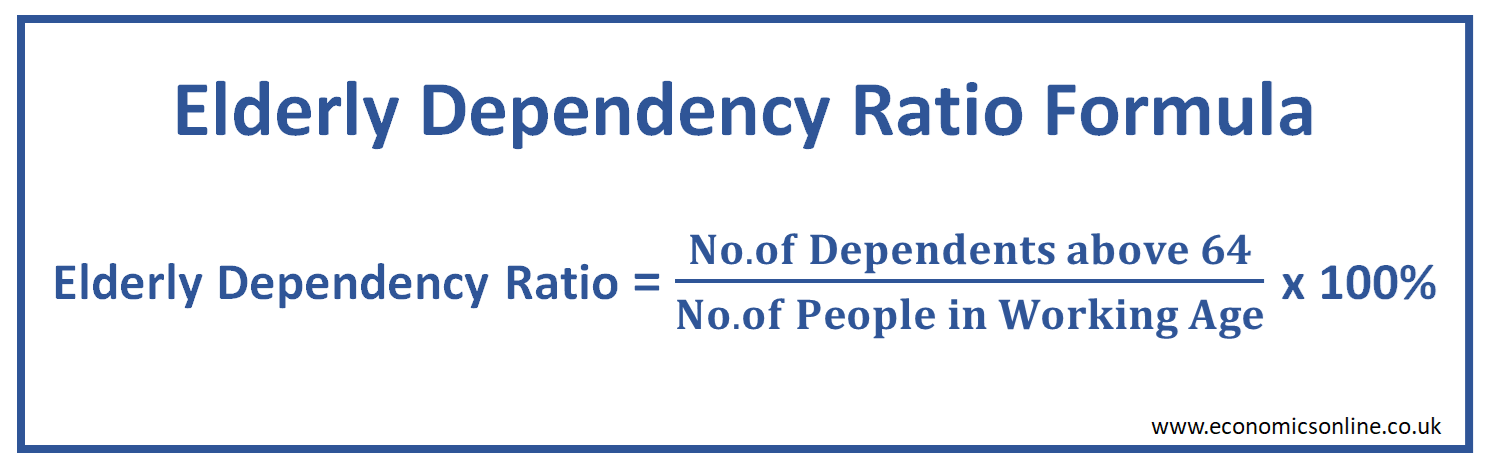
Elderly Dependency Ratio = (Number of Dependents above 64 / Number of people of Working Age) x 100%
A high elderly dependency ratio means a higher level of government spending in pensions and health care.
The main focus of dependency ratio is to separate those of working age, from 15 to 64 years of age, from those of non-working age. It also provides an accounting of those who can earn their own income and who are most likely unable to earn their income in a country. Many complex employment regulations make it possible that individuals under the age of 15 are unlikely to get employed for any personal income. Those who normally entered the age of 65 years are considered in a normal retirement age category, and they are not considered as a part of the workforce of a country. Those who fall in the dependent age category (below 15 or above 64 years) generally have a lack of income potential, and they are dependent on others for their basic needs to be fulfilled.
Dependency Ratio Analysis
Generally, dependency ratios are reviewed to compare the percentage of the total population, termed as working age, that will provide economic support to the remaining non-working age population. The dependency ratio analysis provides an overview for analysts and economists to track the shifts in the structure and age distribution of the population of a country.
Due to the increase in the population of non-working, those who are working are subjected to increased taxes in order to compensate for the rest of the dependent population. The dependency ratio is often adjusted to understand the accurate dependency because people above 64 years of age need more government assistance as compared to the dependents under the age of 15. When the overall age of the population increases, it can be shifted to reflect the increased needs concerned with an ageing population.
Impact of Female Participation
Many females in Europe are concerned about the increasing trend of dependency ratio. For example, by 2040, the dependency ratio in the United Kingdom is expected to rise to 65%. Therefore, this increase in dependency ratio can be overcome by increasing female participation in the labour market as a workforce, a smaller percentage of people under the age of 18, and a proposed increase in the pension age. These strategies can offset the rise of the dependency ratio in a country.
Importance of Dependency Ratio
The importance of dependency ratio is because it compares the ratio of economically inactive with economically active. The economically active are those who pay more income tax, corporate tax, more sales, and VAT taxes. The economically inactive (below 15 and above 64 years) tend to be bigger recipients of government spending, like education, healthcare, and pensions.
When a country’s dependency ratio increases, it causes fiscal problems for the government; for example, Italy already had a high financial debt due to an ageing population and a high dependency ratio. A doubling of the dependency ratio is going to cause difficult choices for the ruling government to make.
Good Dependency Ratio
A low dependency ratio is termed a good dependency ratio, which indicates that there are a sufficient number of individuals in the labour force that can support the remaining dependent population. Typically, a lower dependency ratio denotes better healthcare for ageing adults along with higher pensions. But a higher dependency ratio suggests stress on the economy as the dependents are too many in number to be supported by the workforce.
In 2022, the United Arab Emirates had the lowest dependency ratio of about 20.57. Niger had the highest dependency ratio of 105.13. The United States had a dependency ratio of 54.05.
Factors Affecting Dependency Ratio
The following are some factors that affect the dependency ratio:
Age
A primary factor that affects the dependency ratio is age. Age determines who is and is not included in the workforce.
Demographics
Demographics also affect dependency ratio. Therefore, the demographics of a nation are affected by multiple factors, like immigration policies, birth rates, and other previous government policies, like China’s one child policy.
Foreign Workers
Dependency ratio can also be affected by foreign workers. If a country attracts more foreign workers, it will help grow the workforce and economic health.
Birth Rate
The birth rate also affects the dependency ratio. If a country has a high birth rate, then there will be enough individuals to replace a particular portion of the workforce that retires.
Limitations of Dependency Ratio
There are some limitations of dependency ratio:
The dependency ratio only considers age when determining whether a person is economically active or not.
It does not include those people that are under non-working age (above 64), even if they are working, as some people continue to work beyond the age of 64.
Another drawback is that if a person is working or economically active aside from age, it should determine other factors like status as an illness, disability, or student, at-home parents, long-term unemployed and people who take early retirements.
Solutions to Higher Dependency Ratios
The following are some solutions to normalise high dependency ratios:
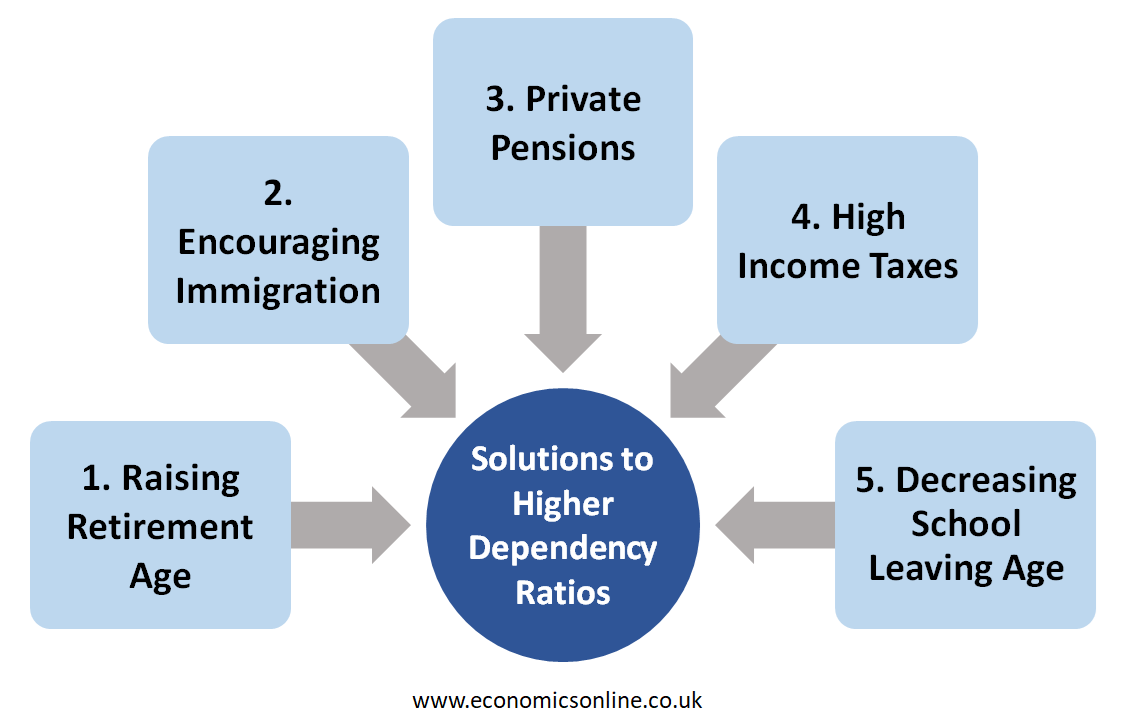
Raising Retirement Age
By raising retirement age, it allows individuals to work for a longer life span and remain economically active.
Encouraging Immigration
Another solution is to encourage immigration of people in their early 20s and 30s.
Private Pensions
By reducing the real value of state pensions and encouraging people to take out private pensions, countries can lower the dependency ratios.
High Income Taxes
The increased value of income taxes makes people able to afford pension and healthcare spending.
Decreasing School Leaving Age
Decreasing the school leaving age can decrease the number of dependents and increase the number of economically active individuals, leading to a lower value of the dependency ratio.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a dependency ratio is a demographic or economic indicator that calculates the number of dependent population aged below 15 and above 64 years, compared with the total population aged from 15 to 64 years. The dependency ratio is used to determine the people of working age and non-working age, which is helpful in understanding taxation, which impacts the government’s revenue and other multiple factors of a nation. The ideal dependency ratio is the lower one, as it indicates less of a burden on the workforce in supporting those who are economically inactive or non-working.


